
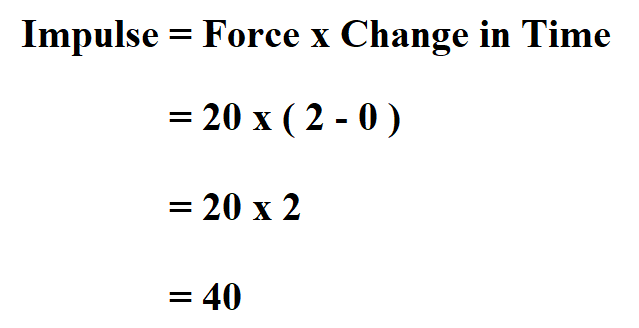

The Impulse of an object is equal to the change in momentum of the object. Numerically impulse is the product of force and time. What is the impulse A large amount of force acting on an object for a short time interval is called impulse or impulsive force. This enables us to solve for the maximum force.ĭefine upward to be the + y-direction. The SI unit of impulse is Newton-seconds(Ns) or kg m/s. Next, we choose a reasonable force function for the impact event, calculate the average value of that function (Figure), and set the resulting expression equal to the calculated average force. We then use the relationship between force and impulse (Figure) to estimate the average force during impact. Using the given data about the meteor, and making reasonable guesses about the shape of the meteor and impact time, we first calculate the impulse using (Figure). Therefore, we’ll calculate the force on the meteor and then use Newton’s third law to argue that the force from the meteor on Earth was equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. It is conceptually easier to reverse the question and calculate the force that Earth applied on the meteor in order to stop it. (credit: “Shane.torgerson”/Wikimedia Commons) The Arizona Meteor Crater in Flagstaff, Arizona (often referred to as the Barringer Crater after the person who first suggested its origin and whose family owns the land). The amount by which the object’s motion changes is therefore proportional to the magnitude of the force, and also to the time interval over which the force is applied. Alternatively, the more time you spend applying this force, again the larger the change of momentum will be, as depicted in (Figure). > Impulse is also defined as the change in momentum with respect to time. The corresponding English engineering unit is the pound-second (lbfs), and in the British Gravitational System, the unit is the slug-foot per second (slugft/s). Clearly, the larger the force, the larger the object’s change of momentum will be. >It is defined as the force acting on a body for very short interval of time. The SI unit of impulse is the newton second (Ns), and the dimensionally equivalent unit of momentum is the kilogram meter per second (kgm/s). So, the same force that acts for a longer duration has more Impulse. t So Impulse also has the dependency upon the time that the force acts for.
Si unit for impulsive force free#
Suppose you apply a force on a free object for some amount of time. Answer (1 of 6): Impulse of a force is the product of force and the time that the force acts for. The purpose of this section is to explore and describe that connection. This indicates a connection between momentum and force. Therefore, if an object’s velocity should change (due to the application of a force on the object), then necessarily, its momentum changes as well. We have defined momentum to be the product of mass and velocity. Apply the impulse-momentum theorem to solve problems.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
